What is wholesale trade?
Wholesale trade is a mode of exchange in which goods are manufactured and obtained in big quantities, then sold in batches to skilled users, resellers, or corporations, but not to end customers.
Wholesaling is an essential aspect of a firm's marketing distribution plan. It entails industrial customer-related preparation for a firm's goods sold to government agencies, distributors, colleges, merchants, hospitals, and other wholesalers.
Highlights
- Wholesale commerce includes only companies that sell to institutions, governments, and other businesses.
- The term "wholesale" does not imply that products are sold to end customers in modest quantities.
- Wholesalers operate in ways that benefit both retailers and manufacturers.
- Wholesalers assist makers in reaching many buyers who are spread over a wide geographical area through retailers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does the term "wholesale trade" mean?
All transactions in which products are bought to manufacture other products, resale, or general business are referred to as wholesaling.
The wholesale trade sector covers the sale of goods produced by mining, manufacturing, publishing, agriculture, and a few other information-related enterprises.
Wholesaling is a phase in the total distribution of items and goods that is considered an intermediate step. A wholesaler sells or manages transactions for the resale of products to other retailers or wholesalers. They may also be in charge of purchasing or selling raw materials, durable consumer items, or manufacturing supplies.
Wholesalers typically offer goods to other businesses from an office or warehouse. However, because the operation is not set up or advertised for that activity, such transactions are rarely carried out through walk-in business.
Generally, the public is not included in the services offered by wholesalers. Instead, they conduct business with merchants or vendors who are part of the broader sales and supply chain.
While wholesale trade is distinct from consumer sales, wholesalers are linked in the supply chain that feeds consumer trade. Wholesalers and their clients may have long-standing relationships, with new orders and follow-ups coming in when suppliers and retailers want more products.
Wholesalers are in the business of purchasing in bulk and delivering smaller amounts to customers. As a result, they can perform physical distribution tasks like inventory management, warehousing, and material handling more efficiently. These also provide timely and consistent pick-up and delivery as needed, allowing wholesale buyers and goods producers to avoid the dangers of storing large inventories.
Wholesale trade intermediaries connect vendors and buyers or carry out commercial operations on behalf of a third party without taking ownership of the goods. Other trade intermediaries, such as trading groups, maybe the owners of products that they sell to their members and affiliates for a very minimal trade margin. Although almost all commodities can be sold wholesale, only a small percentage of them are sold retail.

Source: © Bakhtiarzein | Megapixl.com
What role do wholesalers play?
Wholesalers operate in a way that favours both the retailer and the manufacturer, and they also do a variety of things to make life easier. As a result, wholesalers play a critical role in the economy and the overall trade cycle.
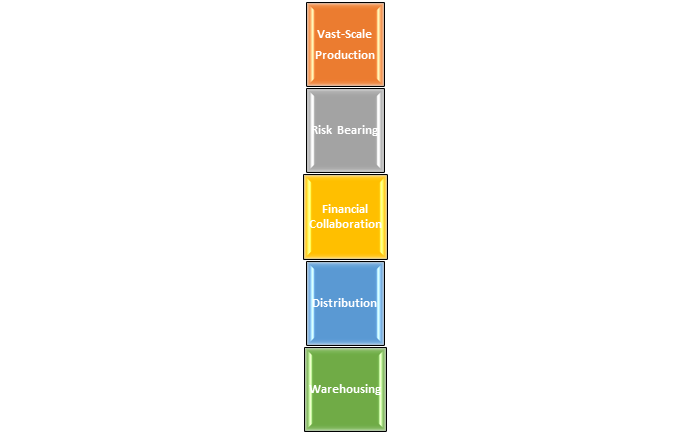
- Wholesalers Services to Producers
Vast-Scale Production: Manufacturers usually produce large quantities of their products, which helps them keep costs down. However, they can do so because wholesalers order in bulk.
Wholesalers will gather small orders from different retailers and place larger orders with the producers. As a result, they can increase their product output without having to worry about waste or warehousing.
Risk Bearing: When a wholesaler buys products from a producer, he also takes all of the risks associated with them, such as spoilage, theft, demand fluctuations, fire, and so on, as well as the cost of insurance. Such risks would remain with the manufacturers until the commodities were sold during the absence of the wholesaler.
Financial Collaboration: Because of how wholesalers operate, they can offer financial help to manufacturers, allowing them to avoid bad debts and free up operating capital. They prefer not to pay cash for their purchases, but they will sometimes pay in advance if a purchase order is quite large.
Distribution: The distribution function is one of the most significant functions in marketing. Wholesalers sell the items to a variety of merchants across a vast geographic area.
Warehousing: Another significant marketing role is warehousing. The wholesaler buys large quantities from the producers and stores them in their warehouses and godowns.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
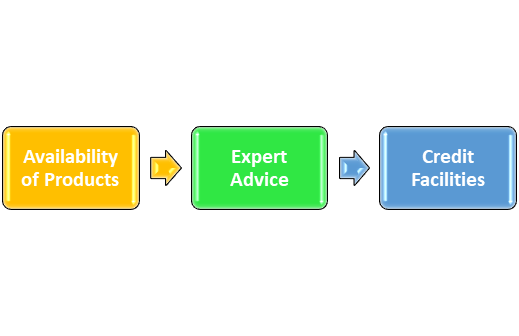
- Wholesalers Services to Retailers
Availability of Products: Retailers should always keep their consumers pleased, so it is crucial that the products in demand are always available, and the wholesalers make this feasible.
Expert Advice: Wholesalers also provide expert advice to retailers on various topics, including new items on the market, proper displaying strategies, and unique product attributes, among others. This will ensure that businesses are constantly on top of their game and can provide their clients with the best services and goods available.
Credit Facilities: While wholesalers do generally not purchase credit products, they frequently make this facility available to retailers. Retailers can grow their scale of operations, thanks to credit facilities, even if they have limited resources and cash.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What is the difference between internal and wholesale trade?
Internal Trade
- Internal trade happens between sellers and purchasers in the same locality, whether it is a city, town, or village.
- Internal trade, which occurs entirely within the same country, can also take place between two or more different states.
Wholesale Trade
- Wholesaling refers to the operations of individuals or businesses who sell vast quantities of goods to merchants and retailers, who then sell them to customers.
- The term "wholesale" does not imply that products are sold in small quantities to end customers.
- Wholesalers function as a crucial link between producers and retailers.
- They assist makers in connecting with many purchasers dispersed across a large geographic area via merchants.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...