What is warehousing?
A warehouse is a business area used to keep raw materials and finished products and plays an essential function in the supply chain. Essentially, it is the complete process of storing physical products in a storage space or dedicated warehouse before they are offered for sale or further distribution.
Warehouses are also known as distribution facilities, where products are distributed again to wholesalers, retailers, or customers directly.
However, once the finished products from the makers and the raw materials from the suppliers arrive in the warehouse, what happens next? This procedure must now determine the location to which these products must be delivered, and they must then be sent down the distribution chain to the consumer.
Moreover, a warehouse must be considered a thriving operation with all the necessary capabilities to give a more profitable return on investment. Some products move slowly while others move quickly during the warehousing process, but all the products in the warehouse must be moved at some point.
Furthermore, warehouse operations are primarily carried out by large corporations. However, for people who have a small business or have just started something new, storing products could usually be done from the house till they have more space. At that time, a firm will need to either rent space for product storage, lease a warehouse, or outsource logistical support to a third party and store products in their warehousing facilities.
In the context of e-commerce deliveries, this is how warehouse operations are carried out. Goods are kept in storage for as long as an order is placed online, after which it is shipped directly to the buyer from the warehouse. So, for example, a product could be temporarily stored in a warehouse in traditional retail before being shipped to a location.
Summary
- A warehouse is a business area that is used to keep raw materials and finished products.
- A warehouse is deemed a thriving operation with all the necessary capabilities to give a more profitable return on investment.
- Product protection is critical in warehouse operations, and a storage room that meets the needs of commodities is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What components comprise warehousing?
While warehousing operations may appear uncomplicated, whether the goal is mere store or storage plus order fulfilment, warehouses require certain elements to assist distributors, manufacturers, and retailers in assessing inventory and safely storing. There are also various processes to guarantee that it is carried out efficiently and that inventory can be moved in and out fast. The elements of warehousing are listed below.
- The most critical resource a company may have to run a successful warehousing operation is space. Hence, when the goods are due to arrive, personnel must prepare for the warehousing operation's execution and determine where goods could be put to make the most efficient use of space.
- Personnel should be ready to receive products as soon as they arrive at the warehouse, and they must be extremely cautious when moving them to the staging area for processing.
- Products must be registered in the warehouse inventory management system so that administrators can keep track of what is presently in stock and accordingly plan for future adjustments.
- After they've been received and processed, all the products must be carefully stored. After that, they must be relocated to their suitable storage site utilising moving equipment.
- Based on the type of the items, warehousing activities are primarily influenced by factors such as pressure, humidity, and temperature. If these factors are overlooked, products may spoil and become unfit for use. For instance, if the products are frozen, they must be kept where the temperature is below freezing. It will lead to better quality depending on the product's storage location and storage within the warehouse premises.
- It's required for the precise placing of existing inventory after new items arrive. Employees are responsible for ensuring that the entire area is used efficiently, and any changes must be monitored and updated in the inventory management systems.
- When the time comes for shipment, the goods must leave the warehouse in the final procedure. Personnel must retrieve, process, package, and load items during this time and then release them from inventory to make room for fresh inbound commodities.

Source: © Endostock | Megapixl.com
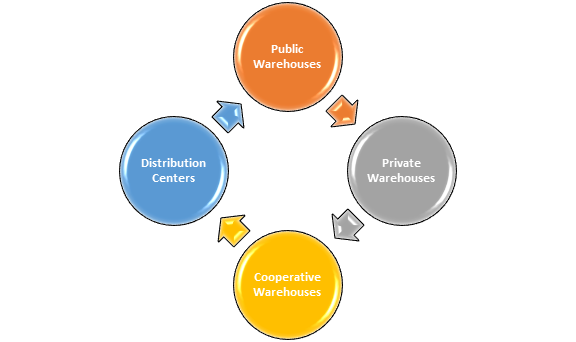
What are the various types of warehousing?
Public Warehouses: These warehouses are managed by a semi-state body or a government. Furthermore, commercial businesses can rent public warehouses to keep their items.
Private Warehouses: Private organisations own and operate these warehouses to keep their equipment and goods.
Cooperative Warehouses: These warehouses are controlled by a cooperative and rent out storage space to private enterprises.
Distribution Centers: Distribution centres take shipments of commodities and promptly transport them from point X to Y.
Source: Kalkine Media
What are the benefits of warehousing?
In addition to the storing of commodities, warehousing is beneficial in a variety of ways.
- It is advantageous to have a warehouse in a central position because if it is close to a manufacturing centre or a consumer, better product transportation will be available, reducing the time it takes to transport goods between different places.
- Inventory accuracy can be boosted by warehousing. It's helpful to know how much inventory is presently accessible and how much has been moved so that future planning can be more accurate.
- Product protection is critical in warehouse operations, and a storage room that meets the needs of commodities is essential. For example, consider the instance of perishable products that require refrigeration and the necessity to ensure that the warehouse meets the standard.
- It is vital to understand how active the company will be over time to achieve optimal labour numbers.
- As the efficiency of a warehouse enriches, more cash can be invested in additional development and cost reduction.
- Knowing the best structure of warehousing and storage of optimal items to shift them quickly creates a good flow of commodities from manufacturer to end customer.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...