What is VAT?
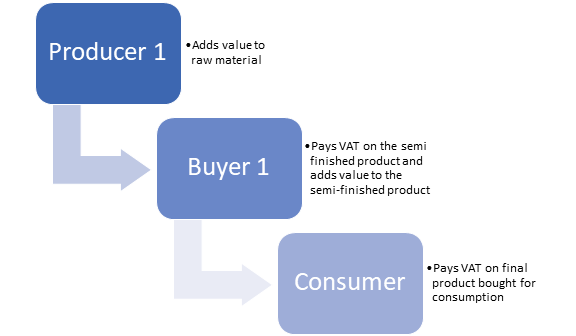
VAT stands for Value-added tax, which is a consumption tax imposed on goods and services. The tax is paid to the government at every stage of production or value addition – from production to sale of the final product. The value-added at each step of the supply chain is identified, and tax is levied on the value-added.
The consumer ultimately pays VAT as sellers at the starting stage of the supply chain gain reimbursement of the taxes they have produced from the subsequent buyer. Therefore, it is also known as the consumption tax.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
Summary
- VAT stands for Value-added tax, which is a consumption tax imposed on goods and services. The tax is paid to the government at every stage of production or value addition – from production to sale of the final product.
- VAT was introduced to eliminate the double taxation system, which was followed earlier.
- VAT is a source of revenue for the government without putting pressure on the wealthy as done by income taxes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why was VAT introduced?
VAT was introduced to eliminate double taxation. Earlier, the tax was levied on every stage of the supply chain on the final product. In effect, the buyer paid the tax which the previous buyer already paid. Ultimately, the consumer paid tax which was already paid.
After the introduction of VAT, the tax was paid on the value-added services only. It resulted in improving the compliance system.
VAT is a source of revenue for the government without putting pressure on the wealthy as done by income taxes. Similarly, VAT is paid by all the consumers.
What are the components of VAT?
VAT is calculated by deducting input Vat from Output VAT.

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
Input VAT – It is a form of tax that the registered dealers pay to the state government monthly. The tax amount is calculated on the raw material purchased by the dealer in a specific month. Generally, registered dealers can claim the VAT paid to the state government.
Output VAT – The consumer pays for the product and services purchase by them. Here, the customers add value throughout the supply chain, for example, wholesalers, manufacturers and retailers.
What does it mean to be registered under VAT?
Manufacturers must register themselves under VAT. Chiefly, manufacturers involve organisations or individuals who are involved in the production. The registration process consists of listing the organisation as a corporation that is qualified for the return of VAT. The registration process can be undertaken through an online platform.
What is the difference between sales tax and VAT?
VAT and sales tax are similar; however, the difference lies in the stages at which these taxes are imposed.
- Sales tax is calculated at the final stage of sales. On the other hand, VAT is collected at every stage of the supply chain or when a good is sold.
- Sales tax is paid by the consumer of the goods and services. However, VAT is produced by the producer, manufacturer, wholesaler, retailer and consumer.
- It is easy to track VAT in comparison to sales tax. Moreover, double taxation can be avoided in VAT.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of VAT?
Advantages:
- VAT cannot be evaded by the taxpayers as it is embedded in the process of purchase and sales.
- VAT is an efficient system to collect taxes and provides a source of government revenue on a timely basis.
Disadvantages:
- It increases the cost for organisations.
- Conflict can be observed between the local and state government in setting VAT across different commodities.
- VAT creates pressure on the lower-income group of consumers as the commodity prices increase until it reaches the ultimate customer.
Who is benefited from VAT?
Traders – Trades can be enhanced as uniform VAT is adopted across the industry.
Consumers – Wealthy and affluent consumers do not have to pay high taxes like income tax.
Government – It is a revenue source, and with a digital breakout, the collection procedure has become easy.
What is the process of VAT collection?
The VAT collection procedure can be divided into two categories: collection method and time of collection. The choice of VAT collection ranges from country to country.
Collection method
- Invoice based – Under Invoice based collection process, the invoices or sales receipts are used to determine the Vat to be paid by an organisation. Every sale receipt mentions the VAT paid by the consumer against the purchase made.
- Account based – The tax is levied on the difference between the revenue and cost of raw material purchased. The data related to revenue and cost of goods sold is computed from the financial statement of an organisation.
Time of collection
- Accrual based – It is a complicated procedure in which the time during the revenue earned, cost of raw material and time of expenses are evaluated. It allows the business to gain an insight into its business performance.
- Cash based – Unlike accrual based, the time at which cash transactions are undertaken is considered. The details of bills are not checked.
Why is GST introduced over VAT in the majority of the countries?
To overcome the cascading effect in the tax system, and to add simplicity in the tax structure, GST (Goods and Service Tax) is adopted by many countries over VAT. However, few products categories are not covered under the GST regime and still follow the VAT regime.
It has been estimated that approximately 160 countries have adopted GST regime which France first adopted in 1954.
GST addresses few disadvantages of the VAT regime. For example, the rate of Vat was different for each state and might create a situation of conflict between the state and local government. However, in GST a uniformed tax rate is imposed across the nation.
The state government had the authority over the VAT collected. Under GST the amount collected through GST is divided between the state and centre government.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...