What are the terms of employment?
The rewards and duties associated with a job that an employee and employer agree on during hiring are referred to as terms of employment.
These "terms" include things like starting wage, working hours, employment responsibilities, dress code, and so on. The employment contract may include benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and life insurance. Employees and employers typically sign written contracts, even if the terms of employment are decided upon verbally.
Summary
- When an employee accepts a job, they commit to the obligations and benefits that come with it.
- Benefits, compensation, corporate policies, retirement, non-compete agreements, and termination are all examples of terms.
- Employees with in-demand abilities typically have some negotiating power over their employment terms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does an organisation's employment term work?
Most companies demand that administrative and professional staff and executives sign a written employment contract or agreement outlining the terms of their employment.
Hourly employees' working conditions are frequently detailed in a corporate policy manual or an employee handbook. Terms can also be communicated verbally in specific situations. Written terms, on the other hand, can safeguard both the employee and the employer.
In addition to the nuts and bolts of perks and compensation, employment conditions might include sensitive subjects like nondisclosure or non-compete agreements, dispute resolution, and termination grounds, as well as the chance of a termination notice.
Job seekers with in-demand abilities can frequently negotiate higher terms of employment. Negotiations between candidates and hiring managers are also a part of executive-level jobs. Whether it's an executive post or an entry-level position, state or federal regulations govern the terms of employment.
Employees with contracts have some job security for the duration of the contract, as far as they don't violate any of the provisions.
It is crucial that an employee read the entire employment contract given by a prospective employer before signing it or get legal advice if there are any doubts.

Source: © Unitonevector | Megapixl.com
What is an employment contract?
An employment contract is a type of agreement between an employee and an employer that describes the nature of their business arrangement, specifically what remuneration the employee will receive in exchange for specified tasks completed at the moment the person is recruited.
There are numerous advantages to have an employment contract when hiring a new employee. It can aid in the retention and recruitment of key personnel. While employers cannot force employees to stay, a contract can ensure that they will give reasonable notice before leaving, which is normally 30 to 90 days.
Employment contracts also aid in protecting crucial trade secrets, which is especially important in high-tech firms. It has the power to restrict employees from soliciting customers or competitors and expose trade secrets.
When an employer has to sell or buy a business, employment contracts can help ensure that key employees do not depart. Employers might pay employees a retention incentive if they stay or warn them that they will forfeit a significant severance compensation if they quit. Employee obligations, bonuses, salary, rights to any discoveries and patents, stock options, expense accounts, and more are spelled out in contracts.

Source: © Miluxian | Megapixl.com
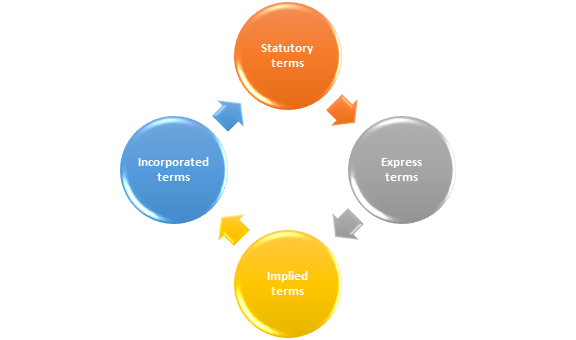
What types of terms can be found in an employee contract?
The following is a list of the various sorts of terms that can be found in employment contracts.
Statutory terms
Statutory terms are those that are enforced by law in an employee's contract. For example, you cannot agree with a worker to offer them less than the applicable national minimum wage or to give them less notice than is required by law.
Express terms
In an employment contract, express terms have been specifically addressed or agreed upon by both parties, such as the number of hours an employee will serve, how much they will be compensated, and how much vacation time they will be allowed.
Implied terms
There could be implied terms in an employment contract if there are no express terms. This means that these terms must be obeyed even if they are not addressed or written down in the contract.
Here are several examples of it:
- Employers must ensure that their workers operate in a safe atmosphere.
- Employees have a responsibility to uphold their loyalty obligations.
- Employees and employers have an implied obligation to establish a mutually trusting and confident relationship.
- Employees must obey directives that are legal and reasonable.
Incorporated terms
Other papers, such as the employee handbook, may have integrated terms into the employment contract.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What are the most common terms of an employment contract?
Even if the contract is simply verbal, all employees are required to have one. When an employee decides to work for an employer, a contract is created that spells out the employee's responsibilities and rights. The right to receive salary and the need to fulfill the employer's instructions are two common instances.
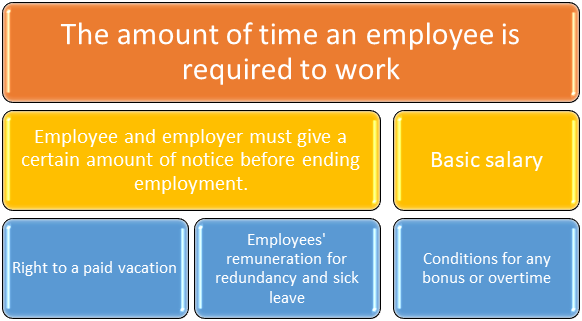
Most workers have a legal right to acquire formal confirmation of their employment contract's main terms, including stated contractual conditions. The following are examples of common express terms:
- The amount of time an employee is required to work can be expressed in terms of days of the week, the total amount of hours per week, or hours per day.
- Basic salary for the employee.
- Right to a paid vacation.
- Employees' remuneration for redundancy and sick leave.
- Conditions for any bonus or overtime, if applicable.
- Employee and employer must give a certain amount of notice before ending employment.
However, the express provisions of an employment contract will have been stated plainly, but they do not have to be included in the written contract. Terms could have been contained during the recruitment process or job announcement, in the handbook or an office manual, or any other materials provided to the worker by the company.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
How do countries determine terms of employment?
Specific standard employment terms have been established in the majority of developing and developed nations.
The Terms of Employment Act in Ireland lays outlaws covering a wide range of workplace and labour issues. The Fair Work Ombudsman of Australia establishes salary, redundancy, rights, leave, and more.
Compared to other regions of the world, labour regulations in the United States are not as liberal. In the United States, most employment contracts are regarded at will, which means that either the employer or the employee can lawfully end the contract at any moment for nearly any reason. Employees who are employed at will can be fired at any time, even if no terms of employment have been broken.
Workers in the European Union are required to take at least four weeks of vacation each year. Expectant mothers in Finland are entitled to paid leave for at least six weeks before their due date and for another 15 weeks following the birth of their child.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...