What is a Stockbroker?
Stock Market
The stock market is a virtual marketplace where there a huge number of buyers and sellers coming together to buy or sell the already issued securities of the listed companies or to buy securities before the companies get listed. These transactions can happen between individuals or companies on the respective stock exchange of the country.
Stockbroker
A stockbroker is a registered entity or an institution that is authorized by the affiliated exchange to facilitate the transaction of other individuals. The very basic job of a stockbroker is to handle all the transactions from its clients for buying or selling of securities.
It is not possible for an average individual to directly transact through the exchange. However, high net worth individuals or Proprietary trading firms can do so after becoming registered members themselves.
In a nutshell, a stockbroker acts as a middleman between the buyers/sellers and the exchange and facilitates the execution of transactions.
Why the need for a stockbroker arises?
In the nascent stage of the stock market, probably a few centuries back, the stock exchanges were open for all individuals to come in and tract for their respective transaction. The scenario was okay as there was a minimal crowd of individuals who were dealing in the stock market, and the exchanges could handle the traffic easily.

Image Source: © Kalkine Group
As the financial markets grew with overall economic growth and development, this crowd started to grow manifold and eventually became very difficult to handle. This is where the need generated to have a mechanism in such a way that the ever-growing crowd could be facilitated but at the same time it reduces the burden on the exchanges.
This is where the idea of a “Stockbroker” emerged.
Functions and duties of a stockbroker
The primary function of a stockbroker is to facilitate the transaction on behalf of its clients. But due to the ever-growing demand from the clients, mandatory measures to be taken from a legal perspective and rapid advancement in the fintech space, today brokers are doing much more than their primary function and providing more services and higher value to the investment community. Some of these functions and duties are
- Smooth facilitation of securities transaction
When an individual or an institution wants to transact any listed security, a broker’s job is to provide a robust infrastructure to facilitate a smooth transaction of securities without any technical errors of glitches.
This becomes even more important for High-Frequency Trading (HFT), intraday traders etc. Even the slightest error in the broker’s terminal or infrastructure can cause millions of dollars of losses.
- Investment advisory
With the growing popularity of stock market among young retail individuals, the demand for good advisory service has also increased. Not every individual is equipped with the right knowledge and experience to deal in the stock market, and many of them don’t even have time to do research on their own.
This is where the broker comes in with its large and well-equipped research team to cater to these individuals. Some brokers even do it for free.
- Fraud or scam reporting
In order to protect the interest of the investors and maintain a general faith in the workings of the stock market, the broker should constantly keep an eye on any unusual activity that may result in a scam or a fraud.
If a broker from its client is noticing any suspicious activity, he should immediately investigate the matter or report to the exchange.
- Provides leverage
A broker's primary business comes from the brokerage that is being generated through transactions. In order to increase the business, brokers are also allowed to provide margin or leverage to the clients. This does two benefits as on the one hand, the brokerage business improves, and on the other, the liquidity in the system also improves, which is important for the growth of the financial markets.
For example, If a broker provides leverage of 50%, then a person with $100 can transact up to $150, pumping in additional liquidity worth $50.
- Adheres to the legal regulations
The financial industry is one of the most regulated industries around the world for obvious reasons. Everyday transactions worth millions of dollars take place, and it is not just the duty but the obligation for all the participants to proceed legally.
For the brokers, they have to have KYC information of the clients, shouldn’t provide leverage beyond the exchange defined guidelines as that can create a systematic risk as we have seen in March 2020 crash. Many brokers who went beyond their margin limits ultimately went bankrupt within a couple of months.
Full-service VS Discount broker
Initially, there was only one type of broker, the full-service broker (traditional one). But with the exponential growth in the technological infrastructure and higher than ever penetration of internet, there is another class of brokers that have emerged over the past few years, the discount brokers.
The very basic difference between the two is their cost structure because of a different business model. As earlier, it was not feasible for a retail individual with small capital to invest because of the very high brokerage.
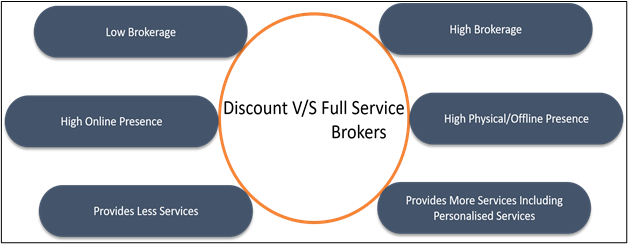
Image source: © Kalkine Group
This primary issue has been taken care of by the discount brokers. Due to the lower cost, generally, the discount brokers do not provide additional services which a traditional broker does like investment advisory service or personalized relationship managers.
The major cost-cutting is done due to extensive emphasis on online presence and procedures, therefore saves a lot of cost on the physical infrastructure. Whereas a traditional broker has a slightly less online presence but can provide better-personalized services at the physical branches
All in all, there are both pros and cons of both types of stockbrokers, and majorly the differentiating factor is cost and services which the investor can pick according to his preference.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...