What is Remote Sensing?
Remote Sensing is the science of sensing an object or phenomenon remotely by measuring reflected and emitted radiations with the help of sensors. Researchers monitor the Earth and other planetary bodies through distant sensors on satellites and aeroplane, providing an overall perspective and information about earth processes. This further empowers information-driven decision support systems regarding our planet’s current and future stages.
Source: Shutterstock
Remote Sensing has an extensive range of advantages spanning various sectors like oil and gas, defence, agriculture, etc.
Principle of Remote Sensing
Remote Sensing detects and discriminates various objects present on the Earth's surface by recording the emitted and reflected energy by the surface of a material. Distinct objects return different energy amounts in different electromagnetic spectrum bands. The technology uses electromagnetic energy which is being incident on the material. The radiance amount is recorded by the sensors and used to interpret the results after processing the recorded signals.
What are the different stages of Remote Sensing?
A typical Remote Sensing process incorporates mainly six steps. The steps are illustrated below:
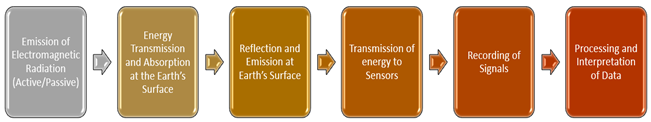
Kalkine Group Image
Evolution in Remote Sensing Technology
Remote Sensing technology first came into existence in 1859 when a French photographer took an oblique photograph from a flying balloon near Paris, giving birth to the remote sensing era. This technique was further followed during the civil war in the US to understand and reveal the defence positions. The innovation was facilitated with technical upliftment like high-quality lenses and airborne usage to strengthen the technology further.
The second phase of development was started during the first World War in Europe, where the camera lenses were used on a large scale for scouting. After getting reliable results, the technology was further explored and used in other study fields too, until the second World War. The most remarkable evolution occurred during the Second World War when thermal, and radar sensing were taken to newer heights.
After 1950, the commencement of Color Infrared technology saw extensive applicability in plant sciences. In 1956, the technology was used to detect plant disease and damage too.
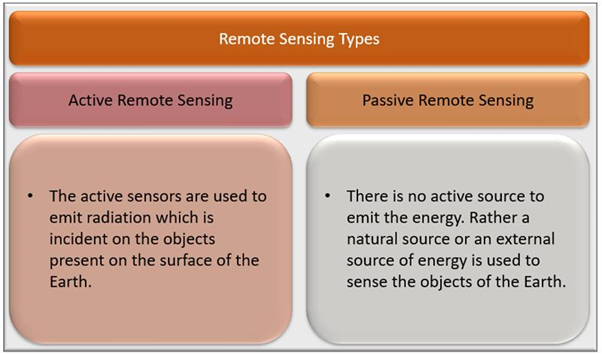
What are the types of Remote Sensing?
There are two main types of Remote Sensing. One is Active, and the other one is Passive Remote Sensing.
Kalkine Group Image
As the name suggests, Active Remote Sensing uses active sensors. Sensors are the active source of energy in this case. The active sensors are used to emit radiation that is incident on the objects present on Earth's surface. The energy gets reflected or emitted and is then received by sensors. This innovation includes microwaves as a functioning specialist as they are impervious to climate conditions.
In Passive Remote Sensing, there is no active source to emit the energy instead of a natural source or an external source of energy used to sense the Earth's objects. This technology uses hyperspectral or multispectral sensors for sensing. The recorded signals are recorded with different band combinations.
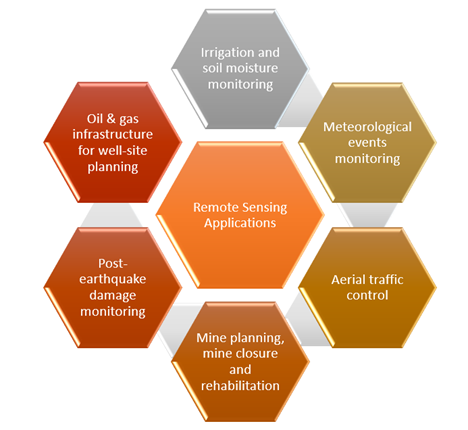
Applications of Remote Sensing
Remote sensing innovation is utilized widely across different fields, including meteorology, topography, hydrology, nature, oceanography, glaciology, and geology. The technology is also used for applications in commercial, military, business, and planning.
Kalkine Group Image
Limitations of Remote Sensing
The inaccuracy of electromagnetic spectrum radiation from the active sensors may affect the target investigation results. Errors from the instruments used in the process may also account for uncertainties in the work. Also, remote sensing is an expensive technique, which may prove to be a limiting factor.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...