What is a JV, or Joint Venture?
Joint Venture (JV) is a commercial agreement between two or more parties to jointly share the possession, expenditure, return on investments, revenue, governance, etc. A Joint Venture is referred to as "JV" in business terms. Organizations expand either by putting more capital into their firm or through a Joint Venture with other organizations.
Understanding a JV
When at least two parties hold hands together to make a favourable collaboration and build a common interest, the newly formed entity is known as a Joint Venture. JVs can be with an organization of the same industry or some other industry or a mix of both. A JV will generate a competitive advantage over other players present in the market.
Each entity of a JV holds a different legal status. A JV might be set up by an agreement that illustrates all the assets, for example, cash, properties, and other resources, every substance will bring to the venture. Likewise, the deal also states how the JV will be overseen and how it can be controlled.
What are the Attributes of a JV?
Positive Teamwork
A joint venture is entered between two parties to complement each other. One party may excel in something in which others might lack and vice versa. The newly formed JV may act as a combined team and work on large scale economies to provide cost-effective solutions.
Shared Risk & Reward
Due to the geographical diversification, the parties going under a JV may have different missions, visions, and goals. The risks and rewards associated with these objectives of any party going for the JV can be shared between them as decided and legally agreed.
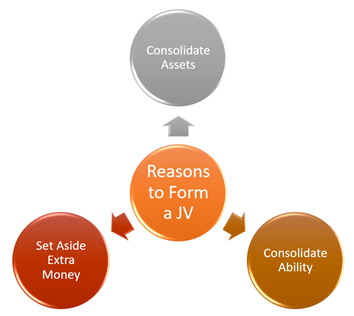
Why do Companies form a JV?
There are multiple reasons why firms go for a JV. Below are some of the primary reasons:
Kalkine Group Image
To consolidate assets:
The JV may have more assets to guarantee the JV’s success than any of the members alone.
To consolidate ability:
JV combines the expertise and consolidates it into a single team which is capable of achieving greater heights. For example, one organization may have an extraordinary group of engineers, another might have good marketing people, and a third may dominate public relations. So, together their abilities may exceed exponentially.
To set aside extra money:
Using economies of scale, the two organizations in the JV can use their expertise to develop a cost-effective solution. This is incredibly viable in technological advancements which are expensive to handle independently. JV members can share the cost, and extra money can be set aside for further development.
What are Basic Requirements for a JV?
The agreement letter must contain the following information but not limited to it.
- Structure of JV
- Objective of JV
- Financial Contributions each party will make
- Transfer condition of asset and resources to JV
- Ownership of Intellectual Property Rights created by JV
- Management and Control
- Sharing of profit, losses, and liabilities
- Dispute resolution clause
- An exit strategy
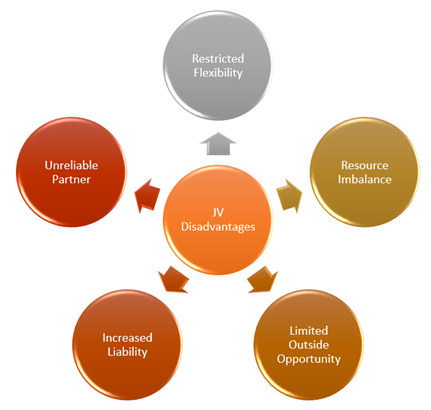
Are there any Disadvantages of forming a JV?
While there are several benefits of entering a joint venture, it has its drawbacks too.
Kalkine Group Image
Restricted Flexibility:
There are times when flexibility is confined in a joint venture. At the point when that occurs, members need to concentrate on JV, and their organizations bear simultaneously.
Resource Imbalance:
Since various organizations are cooperating, there is a significant imbalance of skill, resources, and investment. This can negatively affect the viability of the JV.
Limited Outside Prospects:
JV contracts generally limit the external exercises of member organizations while the venture is in progress. Each organization engaged in a JV might be needed to sign exclusive agreements that may influence current associations with sellers or other business contacts.
Increased Liability:
Most organizations that go into a Joint Venture are set up as a partnership or a limited liability company and work with an associated risk with their picked business partners. Each organization can claim against the joint venture on an equivalent basis despite being involved in the activity that provoked the claim.
Unreliable Partner:
Given the nature of a JV, the members may not commit 100% of their attention in the JV project and become untrustworthy.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...