What is Initial Coin Offering?
Commonly referred to as ICO, initial coin offering is an activity to raise capital in the blockchain and cryptocurrency industry. As the name suggests, it is similar to the concept of an initial public offering (IPO), redefined for the crypto landscape.
A company or a cryptocurrency startup seeking to build a new coin or app can raise funds through an ICO. The process is also known as the token sale.
Interested investors can make purchases in an ICO and receive a token (like shares or stake in an IPO) issued by the company. The token subscribed may offer a stake in the company or provide utility to the products and services provided by the company.
The first ICO was held by open source protocol layer Mastercoin (now Omni) in July 2013. Some successful ICOs are NEO, Ethereum, Alias, Stratis, Ark and NXT.
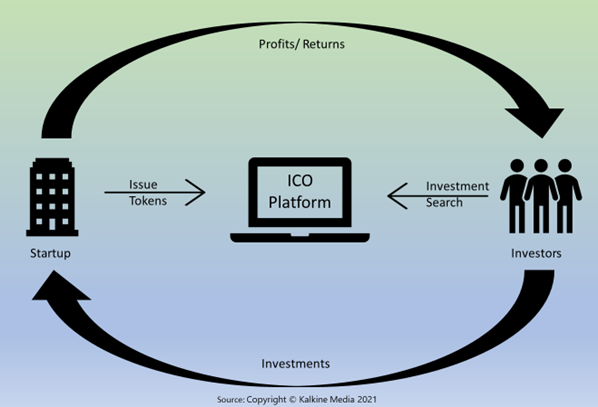
How an IPO functions
How does an initial coin offering work?
Once a crypto startup or company decides to raise funds through an ICO, the first step is to create a whitepaper.
The whitepaper outlines the project and the purpose it will serve once completed, the amount to be raised, duration of the ICO, number of virtual tokens to be kept with founders and what type of money will be accepted (digital or fiat currency).
If the capital requirements mentioned in the whitepaper are met, the amount is further utilized to pursue the project’s goals. If not, the ICO is considered as failed and the capital raised is given back to the investors.
Are initial coin offerings regulated?
As of May 2021, no jurisdiction has implemented any regulation specific to an ICO or tokens. However, regulators have increased their focus on these activities and ICOs are being monitored using a general regulatory regime according to the relevant jurisdiction.
The approach to regulate ICOs varies in every country. Some countries have completely prohibited them, while some are developing the regulations. For instance, according to a report published by law firm Clifford Chance, some regulations are as follows:
- Australia
The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) drafted an information sheet to provide guidance on raising funds through ICOs. The information sheet confirms the legal position of an ICO depending on how it is structured, operated and the rights offered with the token.
If the offering associated with the security offered is covered by the Australian Corporations Act, then it is regulated similarly. If it is beyond the Act’s scope, it will fall under general and the country’s consumer laws.
- United States
ICOs are subject to the US Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) regulations and US security laws. According to these laws, the sale and offer of tokens should be either registered or exempted from registration.
- United Kingdom
The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK has issued several warnings related to ICOs. FCA has stated that whether or not an ICO falls within its boundaries will be evaluated on a case-to-case basis. FCA has also mentioned that ICOs are very risky and speculative investments.
Summary
- An initial coin offering is an activity to raise capital in the blockchain and cryptocurrency environment.
- ICOs are similar to IPOs.
- Any company or cryptocurrency startup willing to build a new coin or app can raise funds through an ICO after creating a whitepaper.
- As of May 2021, the ICOs are governed with little or no regulator interventions. But the security offered may fall under other jurisdictions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the advantages of an initial coin offering?
Some of the benefits associated with ICO are:
- Anyone can participate: In an IPO, only accredited investors having worth of US$ 1 million can participate. However, in ICO, anyone can participate as there are no preconditions required to be fulfilled.
- Token liquidity: The token sold in an ICO has a value, which fits worldwide.
- No middleperson: Once the cryptocurrency is launched, it is made available to all buyers and sellers on the crypto exchange.
- Quick and less expensive: Founders can raise funds through an ICO quickly when compared to other traditional methods. An ICO is less expensive than other conventional routes of raising funds, mainly because it is traded online. For instance, in 2014, Ethereum raised US$ 2.3 million in the first 12 hours of launching.
- What are the disadvantages of an initial coin offering?
- There are many investors who invest in ICOs in the hopes of getting instant returns. In the current scenario, most ICOs are unregulated, leading to huge scams and misinformed investors becoming its victims.
- ICOs are easy to hack. Fraudsters may send phishing emails or hack the issuer’s IT systems. For instance, Mt Gox was hacked in 2014.
- A fraudster may choose the pump-and-dump scheme to earn high profits.
- How does initial coin offering differ from initial public offering?
Under an ICO, a startup tries to sell an idea or the concept of a project to enter the market. In an IPO, an already established private company dilutes its shareholdings to the public.
An ICO involves the sale of coins or tokens, tokenized securities (shares in a business) and utility tokens. On the other hand, an IPO dilutes the ownership of founders by issuing selling shares.
- What are Security Token Offerings?
Tokenized securities (also known as security tokens and tokenized stocks) are digital cryptocurrencies or tokens representing equity shares in an organization. These tokens offer the same benefits as traditional securities and, in addition, the benefits related to digital currency like transparency, instant settlement, etc.
Security token offering (STO) is the offering of tokenized securities on the cryptocurrency exchange or security token exchange. STOs are issued in compliance with the legislation in the location where they are offered. They are of three kinds:
- Equity Tokens
- Debt Tokens
- Asset-backed Tokens
Praetorian Group was the first firm to register the platform with the SEC to offer an STO in March 2018.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...