What is business exit strategy?
A business exit strategy is a process through which investors, founders, or entrepreneurs who have spent considerable sums of money in startup businesses transfer control of their firm to a third party. This is how investors receive a return on investment in a firm. Management or worker buyout, stock sales or purchase by another firm are among popular exit strategies.
Moreover, an exit plan empowers entrepreneurs to reduce or eliminate their ownership share in a firm. A solid exit plan can assist the owner make a significant profit if the business is thriving. Exit strategies assist business owners in limiting their losses if the company fails. An exit strategy can be employed by an investor, as a venture capitalist, to plan for a cash-out.
It's never too soon to start planning ahead of time. Even if it's a small firm, it's a wise idea to plan and think about how you'll transfer ownership of the firm in the future, whether you decide to try to scale it, sell it or and be bought.
Furthermore, the exit strategy may impact several aspects of the business, like the types of revenue models that must be implemented, legal structure, the types of investors required, the trade-offs between investing for short-term vs. long-term growth, etc.
Although exiting could be anything from burnout to business failure to weariness with the firm, it is still helpful to plan before the exit. Business owners can increase their take-home return on investment and sweat equity by thinking logically about possible exit strategies from the start.
Highlights
- An exit strategy is a process through which investors, founders, or entrepreneurs transfer control of their firm to a third party.
- Management or worker buyout, stock sales or purchase by another firm are among popular exit strategies.
- The exit strategy may impact several aspects of the business, like the types of revenue models that must be implemented, legal structure, the types of investors required etc.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the various types of business exit strategies?

Source: © Scanrail | Megapixl.com
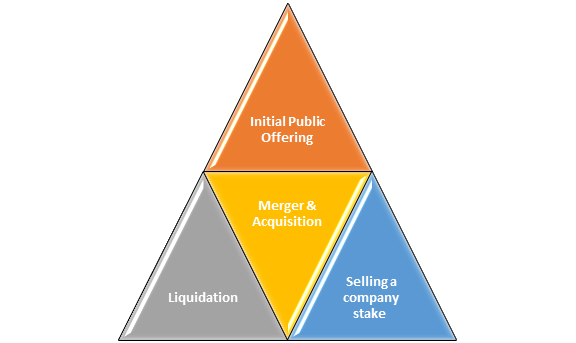
Initial Public Offering
The first selling of a corporation's equity to the general public, sometimes known as "going public," is an IPO or initial public offering.
It's a common exit strategy for startup enterprises looking to grow. Following an IPO, entrepreneurs could choose to stay onboard or sell their company.
Merger & Acquisition
Through a merger, the two corporations merged to form a single firm. As a result, mergers strengthen the value of a corporation, and that is why investors prefer it.
You will become a manager or owner of the new corporation as a result of a merger. It's possible that the newly amalgamated corporation would hire your personnel. Before you plan to merge your firm, be sure the new one is suitable for your existing one; otherwise, you may lose revenue.
When a corporation purchases another firm, it is known as an acquisition. When you have an acquisition exit strategy in place, you relinquish ownership of your corporation to the firm that is buying it from you.
There are two main types of acquisition, one hostile and the other friendly. If you agree to be acquired by a more prominent company, this is called a friendly acquisition. A hostile purchase, on the other hand, indicates you disagree.
To finalise the transaction, the acquiring company buys stakes. If an acquisition is to be used as an exit strategy, it must be conducted friendly.
Furthermore, being purchased by another company could be a lucrative exit strategy for entrepreneurs. You may be capable of attracting suitable purchasers and dominate price conversations if you plan a higher business valuation.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Liquidation
Liquidation would be another option for small enterprises looking to exit. Liquidation is the process of ending your business activities and selling your assets. Investors and creditors get the liquidation value of the company's assets.
Because you do not have to merge or negotiate your business, liquidation is a simple exit strategy. However, if you decide to liquidate your own company, you will lose your business philosophy, consumers, and fame. In contrast to other exit strategy options, your business will not continue to exist.
Selling a company stake
Selling your stake to your partner if you're not the only owner of the corporation is a quick and painless exit strategy. If you engage in a family business, you can develop a succession plan that outlines tactics for a family member or close person to take over the organisation.
What is the importance of exit strategy in a business?
Even if you have no plans to exit your company anytime soon, it's crucial to think about your options and have a plan in place.
The following are the two main reasons for this.
- External investors may undertake realistic estimates of the timeline and expected return on investment with a solid exit plan, which raises the possibility of VC or angel investment.
- Having a concrete strategy assists the owner to structure the firm in such a way that the return is maximised in the event of an exit.

Source: © Peshkov | Megapixl.com
Every company needs to have an exit strategy at a certain point, even if it entails transferring ownership of the corporation when one owner retires. Exiting a firm may be a terrible experience, and emotions can impair judgement. Having a solid exit strategy in place ahead of time will enable you to deal with challenging situations logically.
When developing an exit strategy, consider the following factors:
- The duration of time you intend to be a part of the company.
- Expectations and financial status.
- Any creditors or investors who must be compensated, and how that process will be carried out.
Furthermore, developing a clear exit strategy in place at an early stage may assist you in making decisions that will facilitate your possible exit and make the process as simple and advantageous as feasible.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...