What is a Breakthrough Therapy designation?
Breakthrough Therapy designation is a process devised for accelerating the development and evaluation of drugs/medicines meant for the treatment of severe diseases. To obtain a Breakthrough Therapy designation, a drug must have initial clinical data indicating it may show considerable improvement over already existing treatments based on clinically significant endpoint(s).
For establishing whether the improvement over the existing treatment is significant is based on judgment. The decision considers the extent of the treatment effect (including duration) and the significance of the observed clinical outcomes. Generally, the initial clinical data should demonstrate a clear advantage of the drug over existing treatment.
The clinically substantial endpoint generally indicates an endpoint that gauges an effect on symptoms indicating severe consequences of the indication or irreversible mortality or morbidity (IMM).
A clinically substantial endpoint can also look at the findings indicating an impact on IMM or severe signs, comprising-
- An impact on a recognized surrogate endpoint.
- An impact on a surrogate endpoint or a clinical endpoint deemed likely to forecast a clinical advantage.
- A substantially superior safety profile as compared to already existing treatments (like for an oncology agent less dose-limiting toxicity), with proof of similar efficacy.
- An effect on pharmacodynamic biomarkers that does not fulfil standards for an acceptable surrogate endpoint but indicates the possibility for a clinically profound impact on the underlying indication.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has established four distinctive and successful methods for speeding the availability of drugs that are for treating serious or life-threatening diseases. Breakthrough Therapy designation is part of the four fast-track approaches. The other three approaches are priority review, accelerated approval, fast track designation.
What are the benefits of Breakthrough Therapy designation to the drugs?
The pharmaceutical company or a drug manufacturer request for Breakthrough Therapy designation. If a Breakthrough Therapy designation has not been applied for, the Food and Drug Administration might recommend that the sponsor submits an application requesting for the designation if-
- After assessing submitted data, including initial clinical data), the Agency believes the drug development program could meet the Breakthrough Therapy designation criteria.
- The designation would aid the rest of the drug development process.
To achieve any characteristic of the designation, The FDA should preferably receive the Breakthrough Therapy designation request before the end-of-phase-2 meetings.
Since the primary objective of Breakthrough Therapy designation is developing evidence required to support approval effectively, the FDA does not expect that the designation requests would be made after submitting an original new drug application or biologics license applications (BLA) or a supplement. Once the Breakthrough Therapy designation request is received, the FDA will respond within the next 60 days.
A drug that has been granted Breakthrough Therapy designation is qualified for:
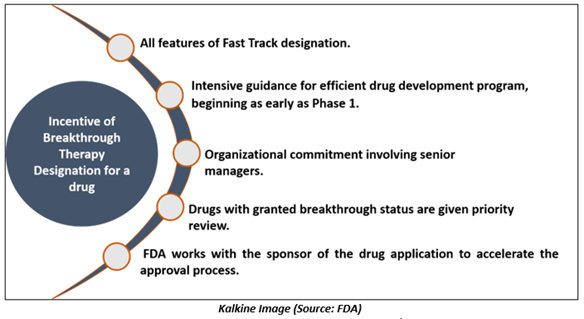
Differences between the benchmarks for fast track designation and Breakthrough Therapy designation
Fast Track designation and Breakthrough Therapy are intended for advancing the drug development as well as the review of drugs for lethal diseases.
However, there are differences related to the requirements to be determined for qualification for the programs.
A Breakthrough Therapy designation is for a drug that treats a life-threatening or serious disease, and initial clinical data shows that the treatment might show considerable improvement on a clinically significant endpoint(s) as compared to the existing therapies.
A Fast Track designation is for medicines that is for a fatal or serious disease, and clinical/nonclinical data show the potential for tackling the unmet medical needs.
What is the deadline for a sponsor to submit a request for a Breakthrough Therapy designation?
The Food Drug and Cosmetic Act says that a Breakthrough Therapy designation request could be made simultaneously with, or later, the application submission for the investigational new drug (IND).
To increase the advantages of the program, the FDA urges drug manufacturers to submit the applications by the end-of-phase-2 meeting. The application should be submitted before clinical trial commencement that will help assess the efficacy of the drug.
Few Recent Examples of Drugs Receiving Breakthrough Therapy designation
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corp Granted Breakthrough Therapy designation for capmatinib
Novartis Pharmaceutical received a grant from the FDA for capmatinib. The drug is being developed for treating adult individuals having metastatic non-small cell lung carcinoma.
Genentech Inc Received Breakthrough Therapy designation for two drugs
Genentech received Breakthrough Therapy designation for bevacizumab and atezolizumab. These drugs, in combination, are used for treating patients suffering from unresectable or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma who have not had any prior systemic therapy.
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc received Breakthrough Therapy designation for avapritinib
The FDA granted Breakthrough Therapy designation to Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc for the development of avapritinib. The drug is indicated for the treatment of adults having unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor harboring a platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha exon 18 mutation, as well as PDGFRA D842V mutations.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...