What are biologics?
Biologic drugs or biologics are produced from living organisms or comprise components of any living organisms. These are genetically engineered proteins targeting specific parts of the immune system to treat the medical indication.
Biologics or biological products have significantly improved the treatment of diseases such as anemia, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), leukopenia, and several forms of cancer. The first biological drug was human insulin and was marketed in 1982.
Biologics include a comprehensive variety of therapeutic formulations derived from human, animal, or microorganisms by using biotechnology or other cutting-edge technologies. Some examples of biologics include blood & blood components, vaccines, tissues, cells, genes, allergens, and recombinant proteins.
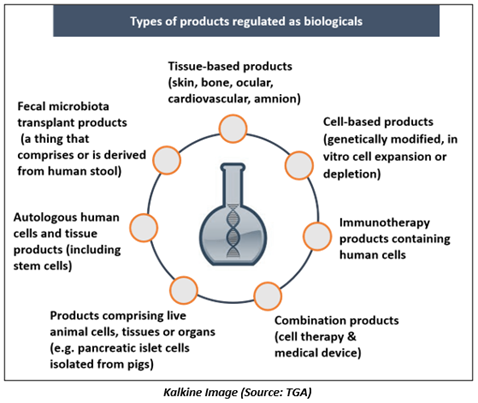
Biological drugs are genetically engineered proteins targeting particular parts of the immune system to stimulate inflammation. Biologics work by interfering with the immune system signals involved in any tissue damage.
How are biologics different from a pharmaceutical drug?
Biologics are manufactured in a living system, for example, microorganism, or animal or plant cells. Many of the biologics are large and complex molecules. Most biologics are manufactured via recombinant DNA technology. However, a drug is usually manufactured through a chemical process, which implies that it is made by mixing specific chemical ingredients in an ordered process.
Biologics, including those prepared by biotechnology, are heat sensitive as well as susceptible to microbial contamination. In distinction, this is not the case for pharmaceutical drugs.
How are Biologics approved?
Like pharmaceutical drugs, for approval of biologics, the application needs to be submitted to the regulatory authorities of the specific countries.
Approval in the United States
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the approval of biological drugs in the United States. Under the US FDA, some biologics are regulated by the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER), while others are regulated by the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER).
A Biologics License Application (BLA) is generally submitted after an Investigational New Drug (IND) or an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE). Relevant studies must be performed before a BLA is submitted. A BLA is a request for permission for distribution of a biological drug across different states.
According to the FDA, a BLA generally applies to vaccines and other allergenic drug products, cellular & genetic therapies, and blood products.
The Biologics License Application is regulated under 21 CFR 600-680. This application is submitted by any legal entity or person who is a manufacturer or an applicant for a license holding responsibility for compliance with product & establishment standards.
Form 356th specifies the requirements for a biologics license application, and this includes-
- Information of the applicant
- Information related to product and manufacturing
- Pre-clinical trials
- Clinical trials
- Labeling
A biologics license application asserts that the biological product is safe, pure, & potent. Also, the manufacturing facilities for a biological drug are inspectable, and each package of the drug holds the license number.
As pharmaceutical drugs require an approved NDA (new drug application), all biologics require an approved BLA for marketing in the US.
Approval in the European Union (EU)-
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) regulates biological drugs. Biological drugs are approved through the centralised marketing authorization process, for instance, products manufactured using biotechnology or advanced therapy medicinal products.
To take benefit of the best available expertise for the evaluation as well as the assessment of biological medicinal products, the agency involves its scientific committees and working parties, including experts from all over Europe. The committees and working parties provide coordination, scientific & administrative support.
Approval in Australia-
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) is accountable for regulating biologics, medicines, as well as medical devices across Australia.
Before biological drugs can be legally manufactured, imported, exported, or supplied in Australia, they must be included on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG).
The ACB (Advisory Committee on Biologicals) directs and makes recommendations to the Health Minister or the Secretary of the health department on-
- Which biological drugs can be included on the ARTG.
- Alterations to entries on the ARTG.
- Removal or continued inclusion of biological drugs on the ARTG.
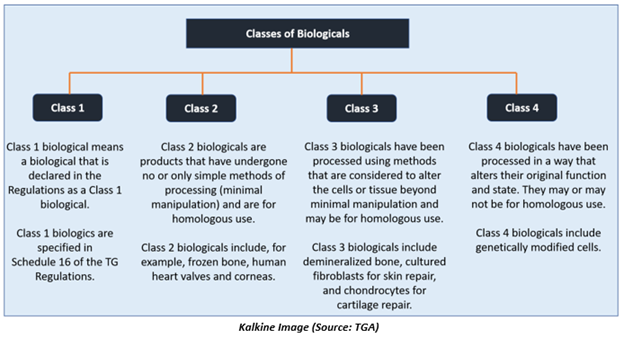
The Therapeutic Goods Administration has classified biologics into four classes:
What are the Risks related to Biologics?
As with many pharmaceutical drugs, biological drugs come with the risk of adverse effect or side effects. The most severe possible side effect of a biological drug is an enhanced susceptibility to infections. Moreover, many biologics have the potential to trigger allergic hypersensitivity reactions.
For patients having disorders that are not life-threatening, the threat of probably serious infection may not be worth the risk. After all, it is not as if adverse events are a rare occurrence.
As biological drugs impair the immune system; hence, for all the patients who are on biologics have a heightened risk of infection. Though, it is of particular concern for patients who take biological drugs for debilitating immune disorders. Biologics are a popular & effective treatment, and many patients might consider the increased risk of infection definitely worth the improvement to their overall quality of life.
However, the side effects of biologics depend on the specific biologic drug and its method of administration into the human body.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...