What is Big Data?
Big data refers to a collection of structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data that organizations collect to mine information that can be used across various advanced analytics applications, including predictive modelling.
Big data is massive and contains multiple complex datasets that are difficult for traditional data processing software to manage. A key advantage of using big data is that the large datasets can be used to tackle complicated business problems that were challenging to address earlier.
INTERESTING READ: Big Data- The Emerging Gold of The Modern Era
What is Big Data Analytics?
Analysis of big data facilitates analysts, business users, and researchers to make fast and better decisions using untapped data. The businesses can use advanced analytics techniques to gain further insights from the earlier untouched data sources independently or together with existing enterprise data.
The advanced analytics techniques include machine learning, predictive analytics, and text analytics, among others.
What are the different forms of Big Data?
There are three types of big data. These are:
- Structured
- Unstructured
- Semi-Structured
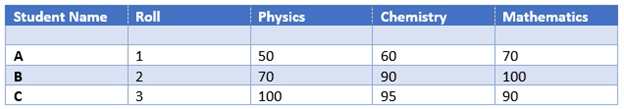
Structured Data:
Structured data are those that can be stored, accesses and processes in a fixed format. An example of structured data is a student database.
Unstructured Data:
As the name suggests, unstructured data have an unknown form or structure. Further, the size of these unstructured data is enormous, and there are multiple challenges while processing such data.
An example of unstructured data is when you do a google search for a topic, say big data. When you run the search, you may get various topics, images, books, authors, different websites, and videos as results. In current times, there are vast data available in an unstructured format, and many businesses fail to derive benefits from such form of data.
Semi-Structured Data:
Semi-structured data has the qualities of both structured and unstructured data. An example of semi-structured data is an RDBMS or relational database management system. Another example would be XML or HTML code used for creating web pages.
GOOD READ: Artificial Intelligence and Big Data- The Powerhouse of a Digital Future
Characteristics of Big Data
- Volume: Big data, as the name suggests, refers to enormous datasets. Which particular dataset falls under the category of big data relies on the volume of data within that dataset. Hence, it is essential to keep the volume of data in mind while handling big data.
- Variety: Variety refers to the various sources and the kind of data. The scope of data is not restricted to spreadsheet and databases anymore but has now become more extensive. The data are now available in various formats such as emails, videos, photos, audio, and blogs.
- Velocity: Velocity is related to the speed at which data is created and simultaneously processed to derive meaningful output.
- Variability: Variability refers to the inconsistency in the data that might exist and impact the process of managing the database efficiently.
Applications of Big Data
Big data is useful for companies to interpret huge data at a faster rate which helps them to take important decisions related to the business, product development, expansion any many more.
Let us look at some of the industry where we can see the application of Big Data across sectors:
- Banking and Securities: In the banking and the securities industry, big data plays a critical role in detecting any fraudulent activity, enterprise credit risk reporting, analytics for trading and so on.
- Insurance: In the insurance industry, big data is useful in providing customer insights for transparent and simpler products. It also helps in better customer retention.
- Communications, Media, and Entertainment: Big data can be used for developing content based on the preference and behaviour of the viewer. Through big data, the companies from the Communications, Media and Entertainment industry can create content for its target audience, recommend related content and also measure content performance.
- Education: In the education industry, big data can be useful for measuring a teacher’s effectiveness to ensure that both teacher and students have a pleasant experience during the session. Data can help make teaching experience better. Further, big data in this industry can help to track the overall progress of the students as well.
- Healthcare Providers: Big data can help the doctors to use evidence-based medicine instead of administering several medical/lab tests to all patients visiting the hospital.
- Manufacturing and Natural Resources: In the manufacturing industry, Big data can be useful in solving the day-to-day challenges faced by the manufacturing companies such as supply chain, the shipment of goods, demand forecasting and many more.
- Retail and Wholesale industry: In this industry, big data support in optimizing staff based in the shopping pattern of the customer, local event. Like many other industries, big data also helps in reducing fraudulent activities and also helps in tracking the inventory.
- Energy and Utilities: Energy and Utilities sectors have now started using smart meter readers that gather data for every 15 minutes. The data can be used to analyze the consumption of utilities by the customers in a better way.
- Transportation: Big data play a crucial role in controlling traffic, route planning, intelligent transport system.
- Government: In the government sector, big data has a massive application. Through big data, the government of any country can look into the socio-economic issues, any fraudulent or illegal activities within the country, health-related issue, and the most affected regions of the country and many more. Based on the output, a relevant decision can be taken, and funds can be provided accordingly.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...